Describe the Structure and Function of Epithelial Tissue
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Epithelial cells are the thin protective coverings that line most organs and cavities within the body.

Lecture Introduction To Epithelial Connective Tissues Youtube Tissue Types Lecture Tissue
They form a surface along which epithelial cells.

. In addition they are in glands. Characteristics of Epithelial Layers. Epithelium is one of only 4 types of human body tissues.
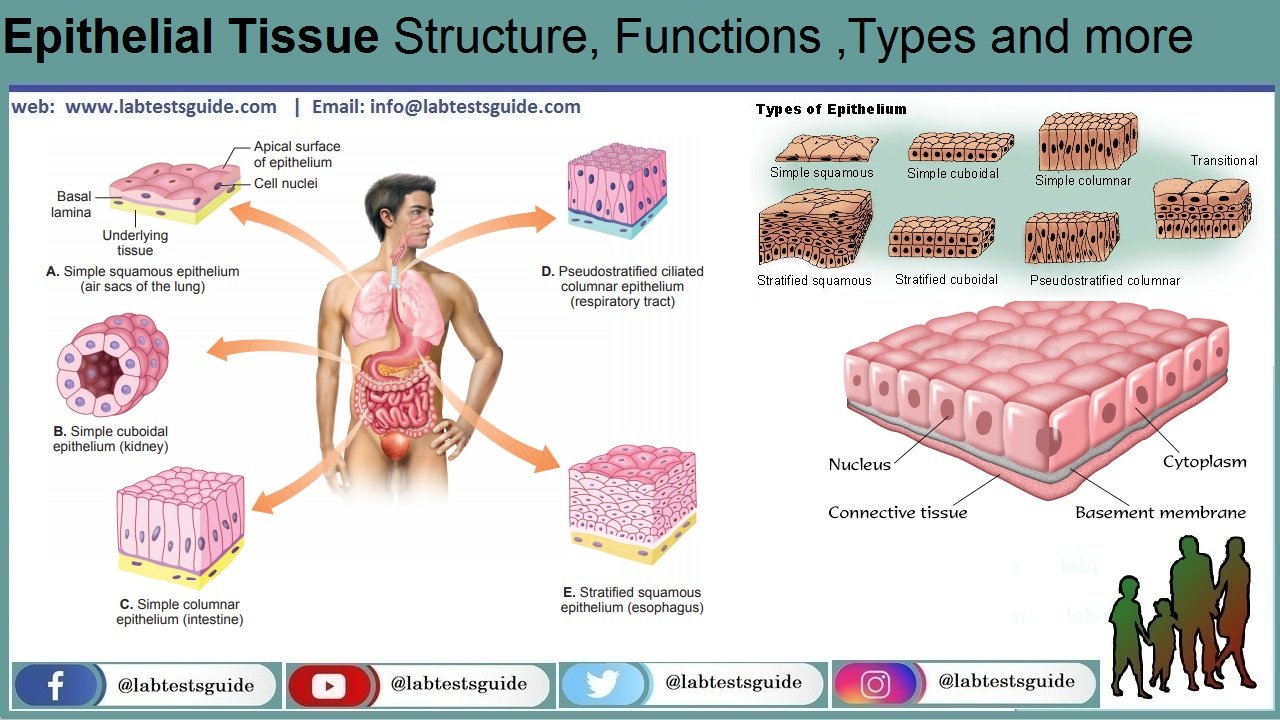
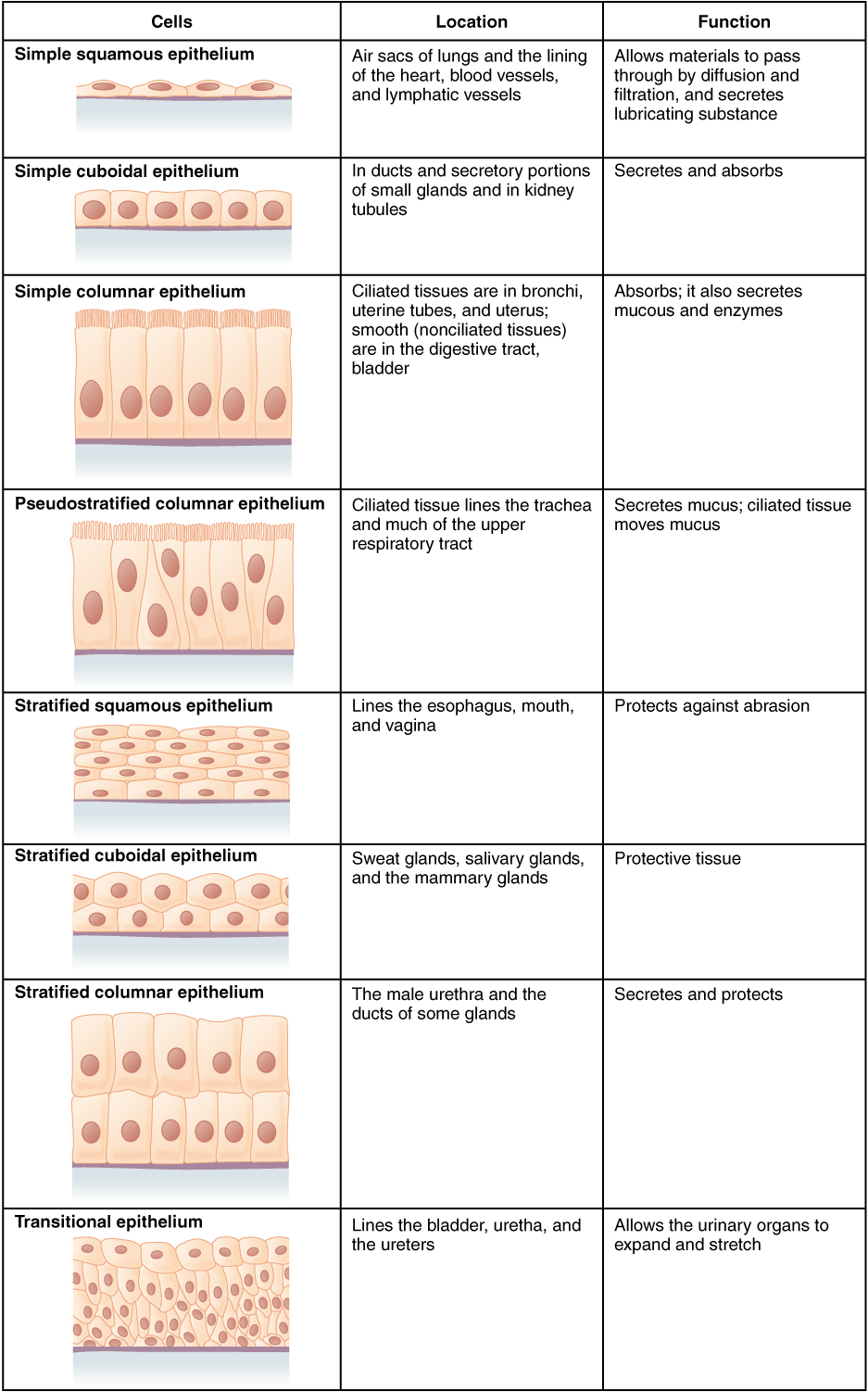
Epithelial Tissue Function. The cells in this tissue are tightly packed within a thin ECM. Tightly packed sheets of cells that cover organs outer surfaces line hollow organs vessels and body cavities Attached on one side and free on the other Can be one or more layers Provides protection from injury and UV light secretion and.
If the most superficial layer of cells is flat the. Epithelial tissue cells are firmly stuffed and structure a continuous sheet. It helps in removing mucus.
It forms a single thick layer and is made of cube-shaped cells. In some tissues a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei this sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. It creates a barrier that helps protect organs and has the effect of absorbing water and nutrients eliminating waste and affecting enzymes or hormones.
Epithelial cells create the covering layer for your body surfaces. Functions of epithelial tissue are secretion. It helps in the secretion of digestive fluids and.
Most epithelia are classified based on two criteria. Start studying Epithelial Tissue. It is these cells tissues and organs that carry out the dramatic lives of plants.
Epithelial cells form the thin layer of cells known as the endothelium which is contiguous with the inner tissue lining of organs such as the brain lungs skin and heart. It helps in the secretion of digestive fluids and absorbs nutrients. Draw diagram of each type of epithelial tissue.
The epithelial tissue or epithelium covers the surface of the organs including the skin trachea reproductive tract and internal walls of the digestive system. These protein connections hold the cells together to form a tightly connected layer that is avascular but innervated in nature. Epithelial tissue covers the cavities and surfaces of the bodys organs.
All glands are made up of epithelial cells. In epithelial tissue cells are closely packed with little or no extracellular matrix except for the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from underlying tissue. Describe the structure and function of different types of epithelial tissues.
Epithelial tissue is composed of cells laid out in sheets with strong cell-to-cell attachments. The epithelial cells are nourished by substances diffusing from blood vessels in the underlying connective tissue. Forming sheets that cover the internal and external body surfaces surface epithelium and secreting organs glandular epithelium.
Epithelial Tissue Function. The skin the lining of the mouth the lining of blood vessels lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all. The shape of the cells depends on the location and function of the tissue.
Describe how the structure of epithelial tissue relates to its function. It also forms a barrier to keep different body systems separate. It forms a uni-layered elongated shaped cells.
Tissues the structure and function of epithelial tissues Can you describe the structure and function of epithelial tissues. The cells of an epithelium act as gatekeepers of the body controlling permeability by allowing selective transfer of materials across its surface. 7 rows It forms a uni-layered elongated shaped cells.
Learn about the types function and structure of epithelial tissue including pseudostratified columnar epithelium and. A thin extracellular layer that commonly consists of two layers the basal lamina and reticular lamina. The free surface of epithelial tissue is usually exposed to fluid or.
Epithelial tissue is a thin layer of cells that cover the surfaces of various organs and cavities in the. It appears 2-3 layered but in actual it is single layered. Like all types it is formed by cells within an extracellular matrix ECM.
It helps in secretions. Plant cells resemble other eukaryotic cells in many ways. To accomplish these dierent functions epithelia come in a variety of structures.
Epithelial tissues provide the bodys first line of protection from physical chemical and biological damage. Epithelial tissue is the thin protective layer of cells which covers the surface of the body and lines the internal organs. They cover organs and body cavities.
Plant tissues like ours are constructed of specialized cells which in turn contain specific organelles. A single layer of cells is called simple whereas a epithelium with two or more layers of cells is called stratified. They cover various surfaces of body parts like the inner lining of the mouth digestive tract secretory glands lining of hollow parts of every organ such as heart lungs eyes the urogenital tract etc.
Epithelial tissue originates from the ectoderm. The main functions of epithelia are protection from the environment coverage secretion and excretion absorption and filtration. They have just a.
The cells of this tissue are generally packed close together. The cells which form epithelial tissue are closely attached to each other through a structure called tight junctions. For example they are enclosed by a plasma membrane and have a nucleus and other membrane-bound.
They are thin tissue that covers all the exposed surfaces of the body. 4 rows There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function. Epithelial cells have many roles in an organism such as playing a part in secretion absorption sensation protection and transport.
Functions of epithelial cells include secretion selective absorption protection transcellular transport and sensing. Epithelial tissue covers the outside of the body and lines organs vessels blood and lymph and cavities. Migrate during growth or wound healing restrict passage of larger molecules between epithelium and connective tissue and participate in filtration of blood in the kidneys.
Shape and layers of cells.
Epithelial Tissue Structure Functions Types And More Lab Tests Guide
Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology

Epithelial Tissue Epithelium Definition Types And Function Tissue Biology Cells And Tissues Anatomy And Physiology
0 Response to "Describe the Structure and Function of Epithelial Tissue"
Post a Comment